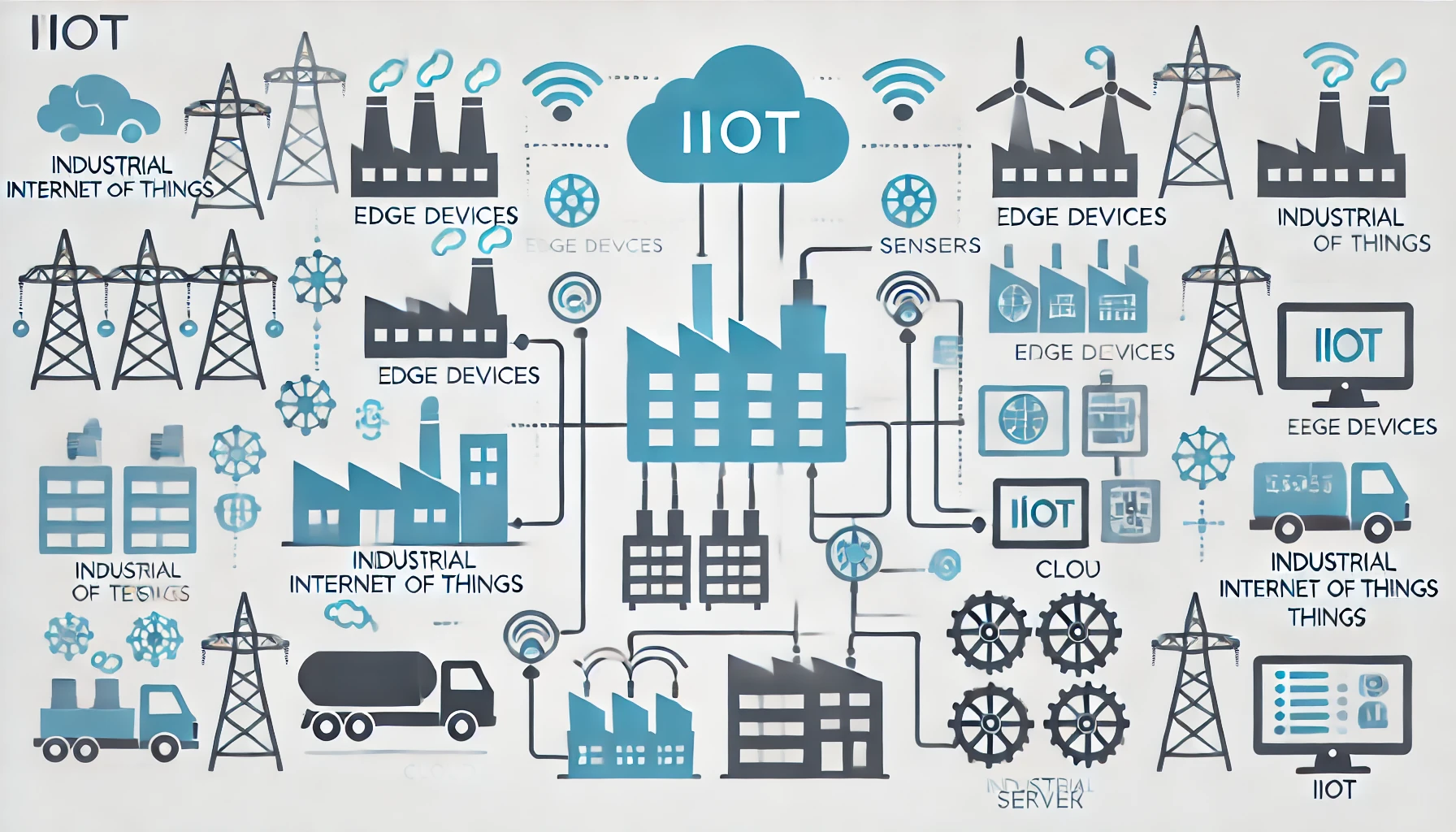
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has become a transformative force in various industries, ushering in a new era of connectivity, automation, and data-driven decision-making. IIoT integrates industrial machines with smart sensors, cloud computing, and advanced analytics to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation. This article explores the architecture, advancements, and applications of IIoT and how it is revolutionizing industries worldwide.
Understanding IIoT Architecture
IIoT architecture is a multi-layered framework designed to connect and manage industrial devices and systems efficiently. The architecture typically comprises the following layers:
1. Edge Devices and Sensors
At the core of IIoT are the edge devices and sensors that collect data from industrial equipment and environments. These devices can monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and vibration. Advanced sensors embedded in machinery gather real-time data, providing valuable insights into the operational status and performance of equipment. The proliferation of affordable and reliable sensors has made it possible to monitor even the most intricate aspects of industrial processes.
2. Connectivity
Connectivity is crucial for transmitting data from edge devices to central systems. IIoT employs various communication technologies, including Wi-Fi, cellular networks, Ethernet, and LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network), to ensure reliable and real-time data transfer. Robust connectivity solutions enable seamless communication between devices, facilitating data collection, analysis, and action. The choice of connectivity technology depends on factors such as data volume, transmission range, and environmental conditions.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data locally at the edge of the network, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. It allows for immediate analysis and decision-making, which is essential for time-sensitive applications. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing minimizes the delay associated with sending data to a central cloud server, enabling quicker responses to critical events. This capability is particularly valuable in scenarios where real-time decision-making is crucial, such as in manufacturing and healthcare.
4. Data Storage and Management
Collected data is stored in cloud-based or on-premises data storage systems. These systems manage vast amounts of data and ensure its availability for analysis. Cloud-based storage offers scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to store and process large datasets without investing in extensive physical infrastructure. On-premises storage, on the other hand, provides greater control over data security and compliance, which is vital for industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
5. Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are applied to the data to extract valuable insights, predict trends, and optimize processes. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. By analyzing historical and real-time data, machine learning models can identify patterns and anomalies, helping organizations anticipate equipment failures, improve product quality, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
6. Application Layer
The application layer provides user interfaces and tools for monitoring, controlling, and analyzing industrial processes. It includes dashboards, mobile apps, and enterprise software solutions tailored to specific industry needs. These applications offer intuitive visualizations and actionable insights, empowering operators and decision-makers to make informed choices. Customizable dashboards and real-time alerts ensure that critical information is always accessible, facilitating proactive management of industrial operations.
Advancements in IIoT
IIoT technology has evolved significantly, driving numerous advancements:
1. Enhanced Connectivity
The development of 5G technology has significantly improved IIoT connectivity, offering higher speeds, lower latency, and increased device density. This allows for more reliable and real-time communication between devices and systems. The higher bandwidth and lower latency of 5G networks enable seamless integration of a larger number of devices, supporting the growing demands of IIoT applications. This advancement paves the way for more sophisticated and data-intensive use cases, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
2. Advanced Sensors
Modern sensors are more accurate, durable, and capable of measuring a wider range of parameters. They are also becoming more affordable, enabling broader adoption. Innovations in sensor technology have led to the development of multi-functional sensors that can monitor multiple variables simultaneously. Additionally, advancements in miniaturization and energy efficiency have extended the lifespan and reliability of sensors, reducing maintenance requirements and operational costs.
3. Edge AI
Combining edge computing with artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled real-time data analysis and decision-making at the edge of the network. This reduces the need for constant cloud communication and speeds up response times. Edge AI leverages machine learning models deployed on edge devices to process and analyze data locally, enabling instant insights and actions. This capability is particularly valuable in applications where latency and bandwidth limitations are critical, such as in autonomous systems and industrial automation.
4. Cybersecurity
With the increasing number of connected devices, cybersecurity has become a top priority. Advances in encryption, authentication, and anomaly detection help protect IIoT systems from cyber threats. IIoT environments are inherently vulnerable to cyber attacks due to their interconnected nature and the criticality of their operations. Implementing robust security measures, such as secure boot, data encryption, and intrusion detection systems, is essential to safeguard IIoT networks and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of industrial data.
5. Interoperability Standards
The development of interoperability standards ensures that different IIoT devices and systems can communicate and work together seamlessly. This promotes a more integrated and cohesive IIoT ecosystem. Standardization initiatives, such as OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) and MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport), facilitate interoperability and data exchange between diverse IIoT devices and platforms. These standards enable organizations to integrate IIoT solutions from multiple vendors, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing system flexibility.
Applications of IIoT
IIoT is revolutionizing various industries by enabling smarter operations, reducing costs, and enhancing productivity. Some key applications include:
1. Manufacturing
IIoT enables smart manufacturing through predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and process optimization. Manufacturers can reduce downtime, improve product quality, and increase operational efficiency. By continuously monitoring equipment health and performance, IIoT solutions can detect early signs of wear and tear, allowing maintenance teams to address issues before they lead to costly breakdowns. Additionally, real-time monitoring of production lines enables manufacturers to optimize workflows, reduce bottlenecks, and enhance overall productivity.
2. Energy and Utilities
In the energy sector, IIoT helps monitor and manage power grids, optimize energy consumption, and integrate renewable energy sources. It also enhances predictive maintenance of equipment, reducing outages and maintenance costs. IIoT-enabled smart grids use real-time data to balance supply and demand, improve grid reliability, and reduce energy losses. Additionally, IIoT solutions enable utilities to monitor the health of critical assets, such as transformers and turbines, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
3. Transportation and Logistics
IIoT improves fleet management, route optimization, and asset tracking in transportation and logistics. It enhances supply chain visibility, reduces fuel consumption, and ensures timely deliveries. Fleet operators can use IIoT-enabled telematics systems to monitor vehicle health, driver behavior, and fuel consumption in real-time. This information allows for efficient route planning, preventive maintenance, and improved fuel efficiency. Additionally, IIoT solutions enable end-to-end visibility of goods in transit, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing the risk of loss or theft.
4. Healthcare
IIoT applications in healthcare include remote patient monitoring, asset tracking, and smart medical devices. It enables better patient care, efficient resource management, and real-time health monitoring. Remote patient monitoring systems use IIoT-enabled wearable devices to collect vital signs and health data, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and intervene when necessary. IIoT also enhances the management of medical equipment and supplies, ensuring that critical resources are available when needed and reducing the risk of equipment failures.
5. Agriculture
Smart farming powered by IIoT involves precision agriculture, automated irrigation, and livestock monitoring. Farmers can optimize resource usage, improve crop yields, and reduce environmental impact. IIoT-enabled sensors and devices collect data on soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. Automated irrigation systems, controlled by IIoT solutions, ensure that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, reducing water waste and enhancing crop yields. Livestock monitoring systems track the health and behavior of animals, improving animal welfare and productivity.
6. Smart Cities
IIoT plays a crucial role in developing smart cities by enabling intelligent traffic management, waste management, and public safety systems. It enhances the quality of urban life and promotes sustainable development. Smart traffic management systems use IIoT-enabled sensors and cameras to monitor traffic flow, optimize signal timings, and reduce congestion. Waste management systems leverage IIoT solutions to optimize waste collection routes, monitor bin fill levels, and reduce operational costs. Public safety systems use IIoT-enabled devices to monitor environmental conditions, detect hazards, and respond to emergencies in real-time, enhancing the safety and well-being of city residents.
Revolutionizing the Industry
IIoT is revolutionizing industries by offering unprecedented levels of connectivity, data-driven insights, and automation. Its impact includes:
1. Increased Efficiency
IIoT enables real-time monitoring and optimization of industrial processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. By continuously collecting and analyzing data from sensors and devices, IIoT solutions provide insights into equipment performance, production workflows, and resource utilization. This information allows organizations to identify inefficiencies, optimize processes, and reduce waste, ultimately improving overall productivity and profitability.
2. Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing data from sensors and machines, IIoT predicts equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance leverages machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies in equipment data, allowing maintenance teams to address issues proactively. This approach reduces unplanned downtime, extends the
lifespan of assets, and lowers maintenance expenses, contributing to higher operational reliability and cost savings.
3. Enhanced Quality Control
Continuous monitoring and data analysis help maintain high-quality standards and reduce defects in manufacturing processes. IIoT-enabled quality control systems use real-time data to monitor product parameters, detect deviations from specifications, and trigger corrective actions. This ensures consistent product quality, reduces rework and scrap rates, and enhances customer satisfaction. Additionally, IIoT solutions enable traceability and compliance with industry standards, facilitating quality audits and certifications.
4. Improved Safety
IIoT enhances workplace safety by monitoring environmental conditions and equipment status, preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. IIoT-enabled safety systems use sensors to detect hazardous conditions, such as gas leaks, temperature fluctuations, and equipment malfunctions. Real-time alerts and automated shutdowns help prevent accidents and protect workers. Additionally, IIoT solutions enable continuous monitoring of safety-critical equipment, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and reducing the risk of penalties and legal liabilities.
5. Sustainability
IIoT promotes sustainable practices by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact across industries. IIoT-enabled energy management systems monitor and optimize energy consumption, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs. Smart water management systems use IIoT solutions to monitor water usage, detect leaks, and optimize irrigation, conserving water resources. Additionally, IIoT-enabled waste management systems optimize waste collection and recycling processes, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices.
The adoption of Industrial IoT is transforming industries by enhancing connectivity, enabling real-time data analysis, and driving automation. Its multi-layered architecture, coupled with advancements in connectivity, sensors, and AI, has paved the way for numerous applications that revolutionize manufacturing, energy, healthcare, and more. As IIoT continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability, shaping the future of industrial operations. By embracing IIoT, organizations can achieve greater operational excellence, improve their competitiveness, and contribute to a more connected and sustainable world.